14 Foods for a Strong Immune System
When colds and flus come knocking on your door, your body will be ready to shut them down.
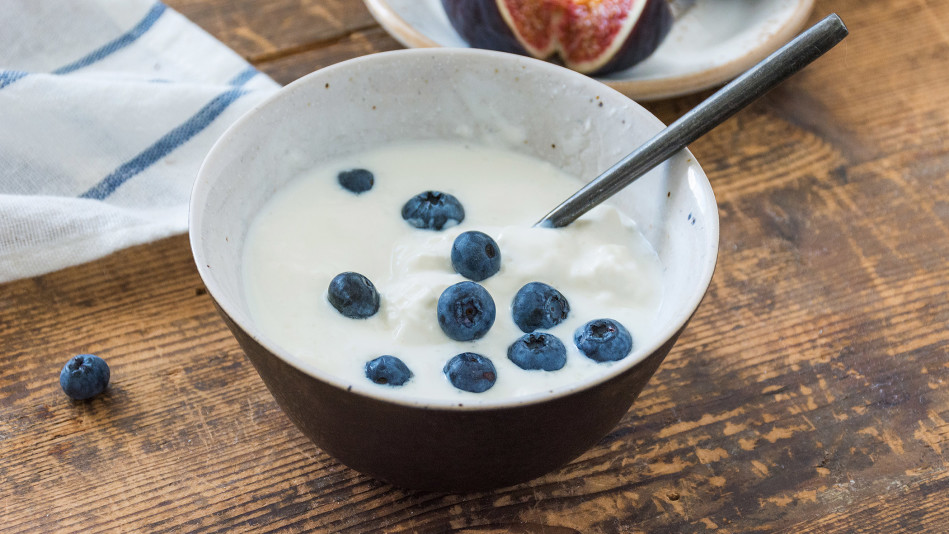

Photo: Vladislav Nosick/Thinkstock
The Key Players in Immunity
Being deficient in any of the nutrients, vitamins, and minerals below can weaken your immune system, making it harder to fend off and recover from illnesses.
Protein
What it does for immunity: If you’re not consuming enough, the function of your T cells, which spot and destroy virus-infected cells, can become impaired.
Vitamin E
What it does for immunity: Immune system cells are more prone to oxidative damage than other cells in the body, says Simin Meydani, PhD, Senior Scientist and Director of the Nutritional Immunology Laboratory at Tufts University. Vitamin E’s antioxidant properties help protect them.
Zinc and Selenium
What they do for immunity: Both minerals help T cells do their job.
Vitamin A
What it does for immunity: The mucus layer in your respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts stands between you and infections. Vitamin A helps keep that layer strong to keep infections out, says Heather Mangieri, RDN, spokesperson for the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics.
Fatty Acids
What they do for immunity: As your immune system mobilizes to fight a virus or infection, your body naturally increases inflammation in the affected area to help the fight. Inflammation-lowering fatty acids help make sure the inflammatory response doesn’t get out of hand and damage healthy cells.
Vitamin C
What it does for immunity: It helps your body build antibodies and cells called neutrophils, which attack viruses and bacteria.
Vitamin D
What it does for immunity: Experts aren’t exactly sure what role Vitamin D plays in immunity, but research suggests that being deficient can make you more likely to contract viruses, says Charles Stephensen, PhD, Research Scientist at the USDA Western Human Nutrition Research Center at the University of California, Davis and an Adjunct Professor of Nutrition at U.C. Davis.
One More: Probiotics
What they do for immunity: A healthy gut seems to help mount a strong defense against germs. A study in Environmental Health found that workers who took a daily probiotic supplement took 33 percent fewer sick days over an 80-day period than colleagues given a placebo.
Where to Get What You Need
Sweet Potatoes/Kale/Butternut Squash/Beets/Leeks
High in – Vitamins A and C
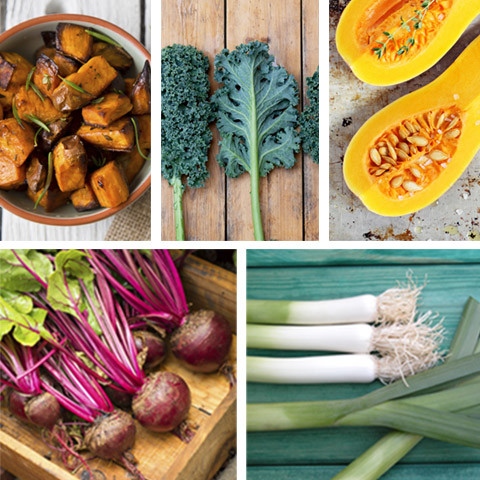

Photo: HausOnThePrairie/zona/los_angela/MarkSkalny/Monika Adamczyk/Thinkstock
Parsnips
High in – Vitamins E and A
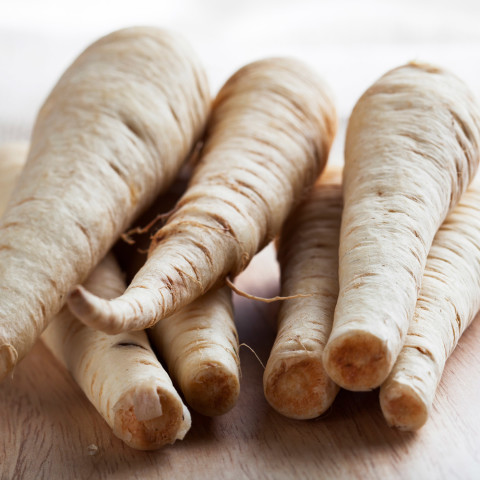

Photo: cheche22/Thinkstock
Canned Fish/Wild Salmon
High in – Protein, fatty acids, vitamin D
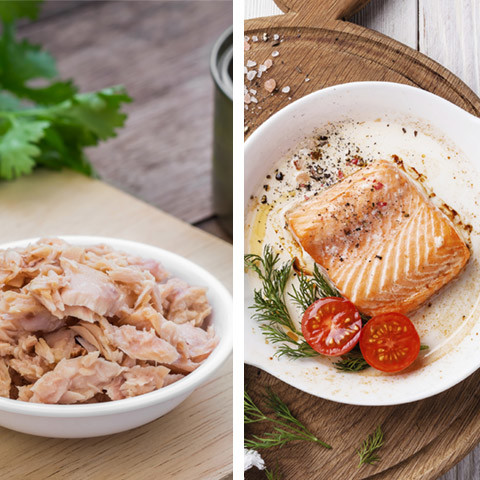

Photo: Amarita/Lisovskaya/Thinkstock
Almonds/Walnuts/Sunflower Seeds
High in – Protein, vitamin E, fatty acids
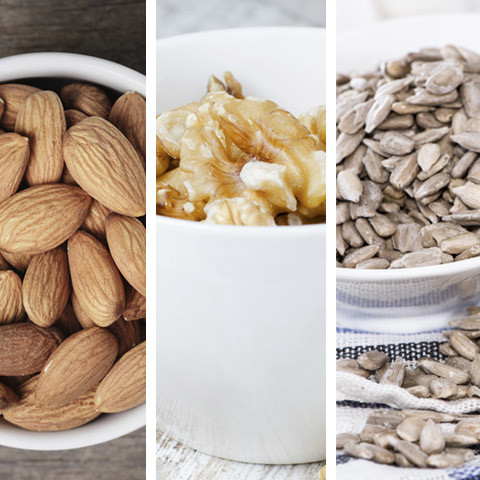

Photo: GooDween123/Shana84/HandmadePictures/Thinkstock
Oysters
High in – Protein, zinc and selenium
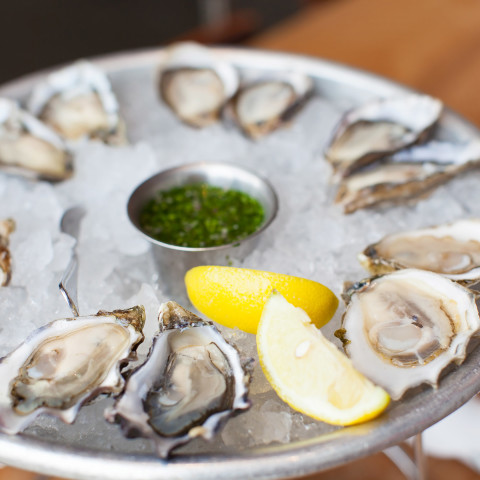

Photo: noblige/Thinkstock
Mushrooms
High in – Zinc and selenium, vitamin D when exposed to UV light (check the label)
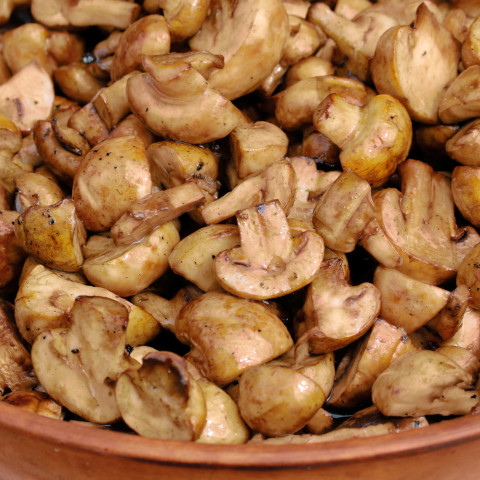

Photo: bwb-studio/Thinkstock
Yogurt
High in – Protein, vitamin A, and probiotics (look for “live active cultures” on the label)
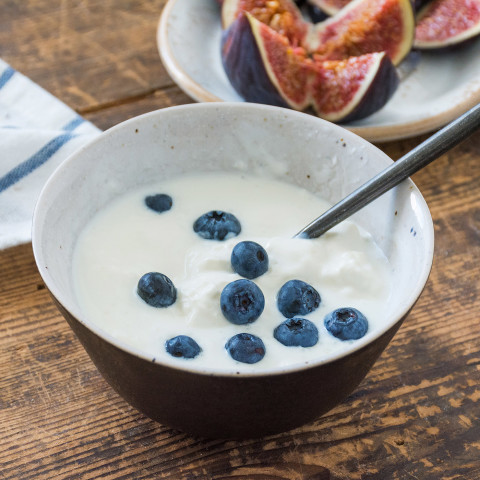

Photo: Vladislav Nosick/Thinkstock
Being deficient in any of the nutrients, vitamins, and minerals below can weaken your immune system, making it harder to fend off and recover from illnesses.
Protein
What it does for immunity: If you’re not consuming enough, the function of your T cells, which spot and destroy virus-infected cells, can become impaired.
Vitamin E
What it does for immunity: Immune system cells are more prone to oxidative damage than other cells in the body, says Simin Meydani, PhD, Senior Scientist and Director of the Nutritional Immunology Laboratory at Tufts University. Vitamin E’s antioxidant properties help protect them.
Zinc and Selenium
What they do for immunity: Both minerals help T cells do their job.
Vitamin A
What it does for immunity: The mucus layer in your respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts stands between you and infections. Vitamin A helps keep that layer strong to keep infections out, says Heather Mangieri, RDN, spokesperson for the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics.
Fatty Acids
What they do for immunity: As your immune system mobilizes to fight a virus or infection, your body naturally increases inflammation in the affected area to help the fight. Inflammation-lowering fatty acids help make sure the inflammatory response doesn’t get out of hand and damage healthy cells.
Vitamin C
What it does for immunity: It helps your body build antibodies and cells called neutrophils, which attack viruses and bacteria.
Vitamin D
What it does for immunity: Experts aren’t exactly sure what role Vitamin D plays in immunity, but research suggests that being deficient can make you more likely to contract viruses, says Charles Stephensen, PhD, Research Scientist at the USDA Western Human Nutrition Research Center at the University of California, Davis and an Adjunct Professor of Nutrition at U.C. Davis.
One More: Probiotics
What they do for immunity: A healthy gut seems to help mount a strong defense against germs. A study in Environmental Health found that workers who took a daily probiotic supplement took 33 percent fewer sick days over an 80-day period than colleagues given a placebo.
Where to Get What You Need
Sweet Potatoes/Kale/Butternut Squash/Beets/Leeks
High in – Vitamins A and C

Photo: HausOnThePrairie/zona/los_angela/MarkSkalny/Monika Adamczyk/Thinkstock
Parsnips
High in – Vitamins E and A

Photo: cheche22/Thinkstock
Canned Fish/Wild Salmon
High in – Protein, fatty acids, vitamin D

Photo: Amarita/Lisovskaya/Thinkstock
Almonds/Walnuts/Sunflower Seeds
High in – Protein, vitamin E, fatty acids

Photo: GooDween123/Shana84/HandmadePictures/Thinkstock
Oysters
High in – Protein, zinc and selenium

Photo: noblige/Thinkstock
Mushrooms
High in – Zinc and selenium, vitamin D when exposed to UV light (check the label)

Photo: bwb-studio/Thinkstock
Yogurt
High in – Protein, vitamin A, and probiotics (look for “live active cultures” on the label)

Photo: Vladislav Nosick/Thinkstock