Dr. Oz: 4 Warning Signs You Should Never Ignore
For some diseases, the red flags are changing. Here's what to watch out for now.
By Dr. Mehmet Oz
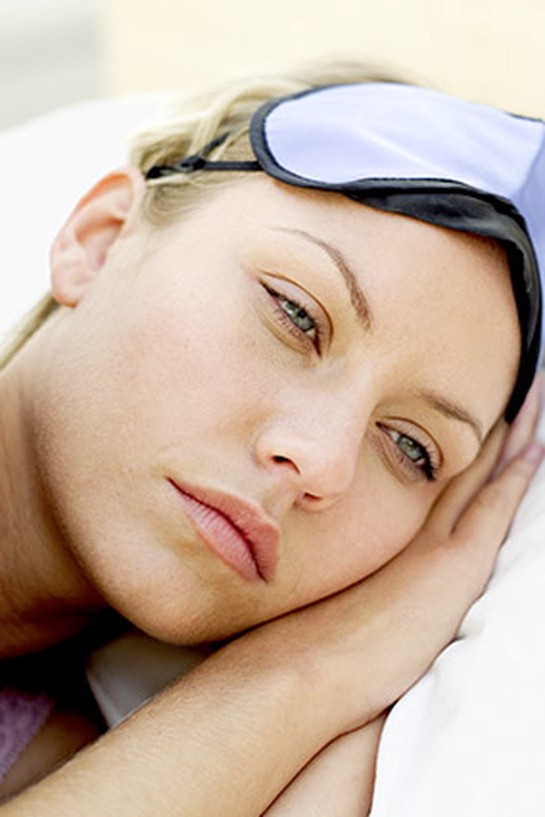
Insomnia
According to research presented at a 2012 American Heart Association conference, insomniacs are twice as likely to suffer a stroke as people who don't have trouble sleeping. Researchers believe that as a person's sleep deficit rises, so does her blood pressure, which, over time, can lead to inflammation of vascular walls. And it doesn't take long for the negative effects of insomnia to set in: Blood pressure can shoot up after even a single night of inadequate sleep. For sounder slumber, try turning on some "pink noise" (think falling raindrops). A small 2012 study found that this blend of sound frequencies, which is more pleasing to the human ear than white noise, can help calm brain waves, leading to 23 percent more restful sleep.
From the February 2014 issue of O, The Oprah Magazine